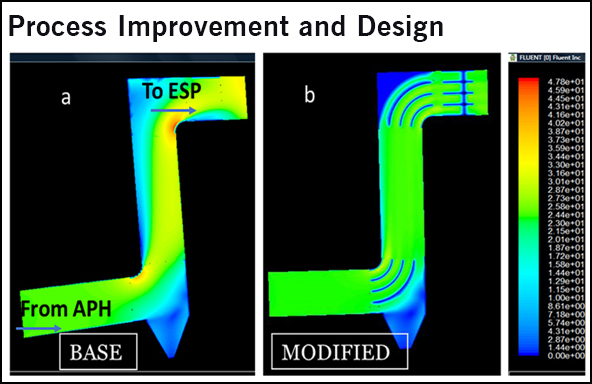
INTRODUCTION
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a simulation tool used for visualizing system/process/equipment parameters through-out the domain. In CFD, an exact geometrical model (1D, 2D or 3D) of the process/equipment is created and divided into very small cells in which process equations are solved. Process equations are to be solved for each cell using numerical methods, for which large computational resource is required. Once solved and validated, CFD model provides a continuous visual profile of all the process parameters. A validated CFD model is like having data from thousands of sensors for each of the process parameters.
A validated CFD model is powerful tool to understand the process and its inherent abnormality and can be used to evaluate the effect of any modification or design changes in the process and before actual implementation. Presently, with high computational power being available, CFD modeling is being used to develop design and processes from conceptual stage to final specifications.
BENEFIT
Benefit accrued in some of the NTPC stations where CFD recommended modifications have been carried out are listed in the following Table
| S. No. | Station | Modification carried in | Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tanda | FG Duct | Reduction of ID Fan Power by 100 KW/Unit |
| 2 | Kahalgaon St-I | FG Duct | Reduction of ID Fan Power by 120 KW/Unit |
| 3 | Simhadri St-I | FG Duct | Reduction of ID Fan Power by 350 KW/Unit |
| 4 | Simhadri St-II | FG Duct | Reduction of ID Fan Power by 330 KW/Unit |
| 5 | Ramagundam ST-II | ESP Internal | Reduction in SPM by 100 mg/Nm3 |
| 6 | Ramagundam ST-II | ESP Internal | Reduction in SPM by 100 mg/Nm3 |

