Thermal Energy Storage Systems (TESS)
Thermal energy storage integrated with thermal power plant can help in avoiding the operation of boiler below technical minimum load by storing excess energy from the boiler by diverting steam through it.
Rationale
The increasing adoption of variable renewable energy sources necessitates that conventional base load power plants, particularly coal-fired plants, adapt to more flexible and variable operational patterns. This flexible operation of thermal power plants has led to several negative consequences like deterioration in heat rate and higher APC at partial loads, increased thermal and mechanical stress, reduced plant life, and higher rates of forced outages. To address these challenges, NTPC is actively seeking solutions to mitigate the adverse effects of flexible operations in thermal power plants. One promising approach is the integration of thermal energy storage systems (TESS), which can store excess energy from the boiler by diverting steam through the storage system.
Scheme
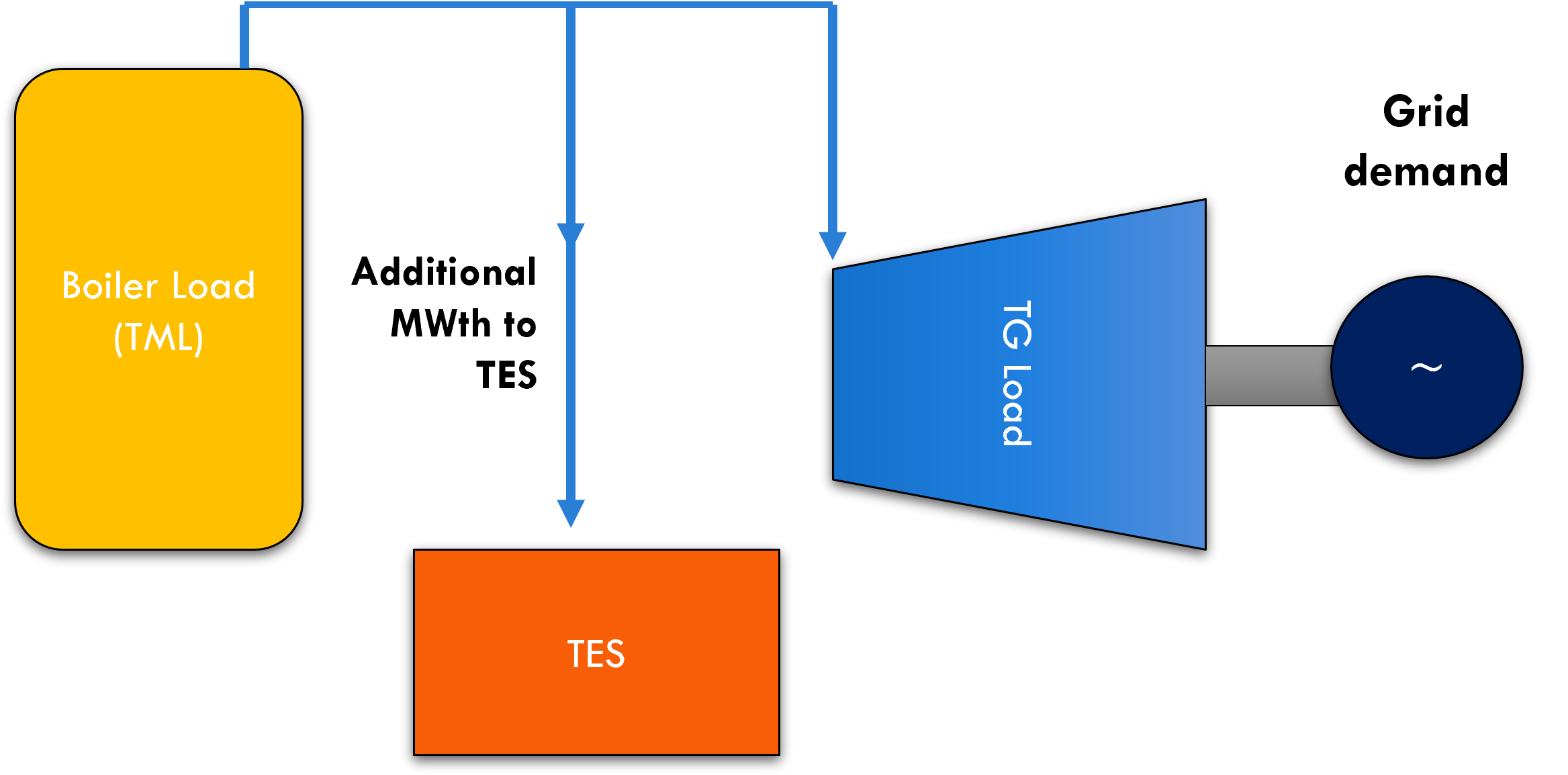
Brief About the Technology/Works being carried out
With the intention of mitigating the adverse impacts of flexibilization on thermal power plants and also to supply additional power over and above the unit capacity during peak demand hours, a pilot project of TESS integrated with Thermal power plant to supply additional power (15 MWe) has been planned by NTPC at its existing thermal power plant in Dadri.
The process consists of two cycles. Charging Cycle and Discharging Cycle.
Charging Cycle: During periods of low demand from the thermal unit, boiler shall be maintained at or above technical minimum load while keeping the TG output as per the grid demand. The excess steam from the boiler shall be diverted to the TESS block, there by charging the storage unit.
Discharging Cycle: During peak demand periods, the TESS shall be operated in a separate power cycle with additional Turbine Generator set. The heat energy stored in the TESS shall be used for generating superheated steam and shall be fed to the TG set to generate power.
Benefits of the Project
- Maintaining the operation of Boiler above technical minimum load there by reducing the detrimental impacts of flexible operation
- Enables smooth integration of Variable renewable energy into the grid
- Providing additional power over and above unit capacity during peak demand hours

